Inbox (3,085) B Engineering Not Untitled document 79/Centricity/Domain/3941/central%20and%20inscribed.pdf engineering-not Math Central Untitled Solve for x: 140 IOx – Find the measure of the arc or angle indicated
Central and Inscribed Angles Worksheet PLEASE SOLVE ALL THE QUESTIONS!!! Inbox (3,085) B Engineering Not Untitled document 79/Centricity/Domain/3941/central%20and%20inscribed.pdf engineering-not Math Central Untitled Solve for x: 140 IOx – Find the measure of the arc or angle indicated
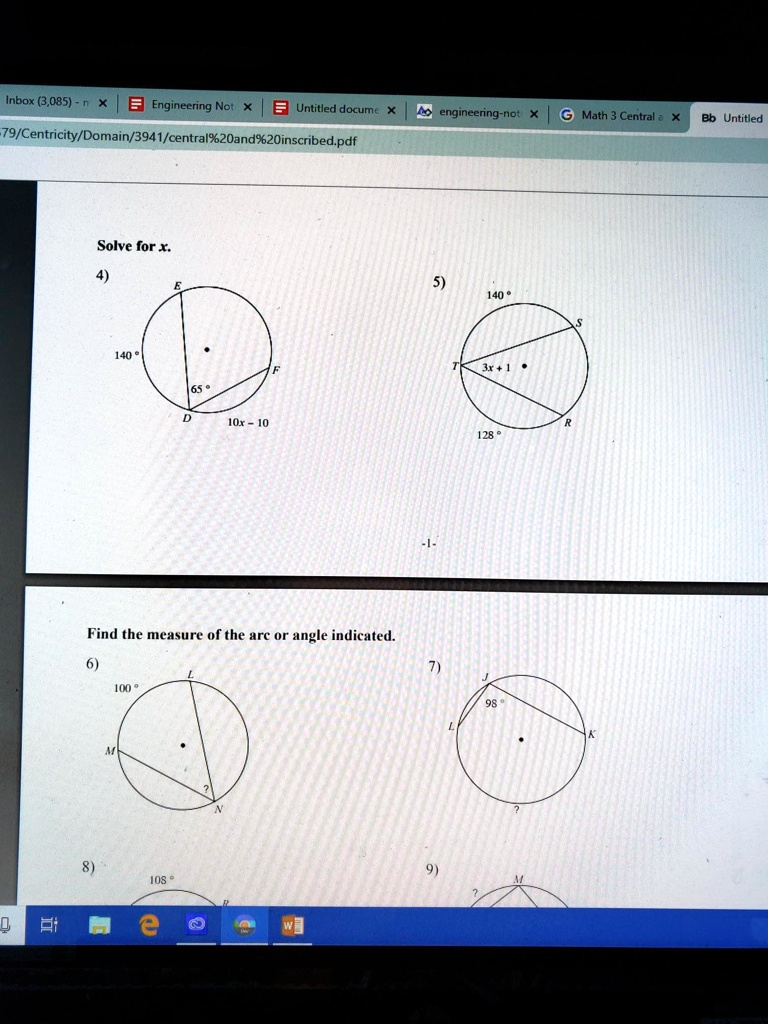
The Correct Answer and Explanation is:
Key Concepts:
- Central Angles: A central angle is an angle whose vertex is at the center of the circle, and its arms (sides) are radii. The measure of a central angle is equal to the measure of the arc it intercepts.
- Inscribed Angles: An inscribed angle is an angle formed by two chords in a circle that share a common endpoint. The vertex of an inscribed angle lies on the circle itself. The measure of an inscribed angle is half of the measure of the arc it intercepts.
General Approach to Solve for xxx:
- For Central Angles:
- If you’re given a central angle (for example, 140°), the measure of the arc it subtends (the arc intercepted by the angle) is equal to the measure of the angle. For example, if the central angle is 140°, the arc it intercepts is also 140°.
- For Inscribed Angles:
- If you’re dealing with an inscribed angle, say you’re asked to find the measure of the angle that intercepts a certain arc, the relationship is: Inscribed Angle=12×Measure of the Arc\text{Inscribed Angle} = \frac{1}{2} \times \text{Measure of the Arc}Inscribed Angle=21×Measure of the Arc
- If you’re given the measure of the arc, you can solve for the inscribed angle by dividing the arc measure by 2. If the angle is given and you’re asked to find the arc, multiply the angle by 2.
Example Problem:
If you’re given that a central angle AOB=140∘AOB = 140^\circAOB=140∘, and you need to find the measure of the arc ABABAB, the measure of the arc ABABAB is equal to the central angle, so:ArcAB=140∘\text{Arc} AB = 140^\circArcAB=140∘
If you’re given an inscribed angle, say ∠ABC=x\angle ABC = x∠ABC=x, and you’re told that it intercepts an arc of 140∘140^\circ140∘, then:x=12×140∘=70∘x = \frac{1}{2} \times 140^\circ = 70^\circx=21×140∘=70∘
Conclusion:
The key is recognizing the difference in how central and inscribed angles relate to the arcs they intercept. For central angles, the measure of the angle is the same as the arc measure. For inscribed angles, the angle measure is half of the intercepted arc’s measure.
