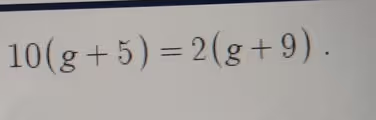
The Correct Answer and Explanation is:
The correct answer is g = -4.
Here is a detailed explanation of the steps required to solve the algebraic equation 10(g + 5) = 2(g + 9).
The goal of solving this equation is to find the value of the variable g that makes the statement true. The process involves isolating the variable g on one side of the equals sign.
First, we must simplify both sides of the equation by applying the distributive property. The distributive property states that a(b + c) = ab + ac. We will apply this rule to both the left and right sides of our equation.
On the left side, we have 10(g + 5). We multiply 10 by each term inside the parentheses:
10 * g = 10g
10 * 5 = 50
So, the left side becomes 10g + 50.
On the right side, we have 2(g + 9). We multiply 2 by each term inside the parentheses:
2 * g = 2g
2 * 9 = 18
So, the right side becomes 2g + 18.
Now, the equation is rewritten as:
10g + 50 = 2g + 18
The next step is to collect all terms containing the variable g on one side of the equation and all the constant terms (the numbers) on the other side. We can start by moving the g terms to the left side. To do this, we subtract 2g from both sides of the equation to maintain the balance:
10g – 2g + 50 = 2g – 2g + 18
8g + 50 = 18
Now, we need to move the constant terms to the right side. We can achieve this by subtracting 50 from both sides:
8g + 50 – 50 = 18 – 50
8g = -32
The final step is to solve for g. Since g is currently being multiplied by 8, we perform the inverse operation, which is division. We divide both sides of the equation by 8:
8g / 8 = -32 / 8
g = -4
To verify the solution, we can substitute g = -4 back into the original equation:
10((-4) + 5) = 2((-4) + 9)
10(1) = 2(5)
10 = 10
Since both sides are equal, our solution g = -4 is correct.
