The Correct Answer and Explanation is:
Of course. Here are the correct matches and a detailed explanation.
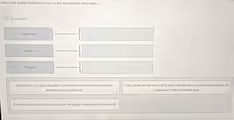
Correct Answer
- Utilitarian: Organizations one joins for some material or tangible personal gain.
- Normative: Organizations one joins based on some shared moral or ethical purpose.
- Coercive: Organizations one is forced to join; often used to resocialize individuals.
Explanation
This classification system for formal organizations was developed by sociologist Amitai Etzioni to categorize them based on the primary reason for a person’s participation. Each type reflects a different relationship between the individual and the organization.
Utilitarian organizations are joined out of practical necessity or for a specific material reward. The term “utilitarian” refers to utility or usefulness. People participate in these organizations to gain something tangible, most commonly a paycheck. A business or a corporation is a classic example; employees work in exchange for salary and benefits. Similarly, a university can be seen as a utilitarian organization because students attend to earn a degree, which is a credential that leads to better career opportunities and financial security. The membership is a contractual exchange of labor or effort for a tangible benefit.
Normative organizations, also known as voluntary associations, are joined because people believe in the organization’s goals and values. Participation is not for material gain but for a sense of moral or ethical purpose. The reward is intangible, such as personal satisfaction, a sense of community, or the feeling of contributing to a worthy cause. Examples include political parties, religious institutions like a church or mosque, and non-profit groups like Greenpeace or the Humane Society. People volunteer their time and resources because they are personally committed to the organization’s mission.
Coercive organizations are characterized by involuntary membership. Individuals do not choose to join these organizations; they are forced to participate. These are often what sociologist Erving Goffman called “total institutions,” which isolate people from the wider society and tightly control all aspects of their lives. The main purpose of many coercive organizations is resocialization, which involves stripping away an individual’s old identity and building a new one that conforms to the organization’s rigid rules. Prisons, military boot camps (especially under a draft), and long term psychiatric hospitals are primary examples of coercive organizations.
